•
A
relationship
•
A
relationship set
•
Descriptive
attributes
•
Instance
•
Role
•
Role
indicators
A relationship is an association among
two or more entities
A relationship set: a set of similar
relationships
Several relationship sets might
involve the same entity sets
Ex. A manager relationship set
involving employees and departments
•
A
descriptive attribute is used to record information about the relationship. Ex.
Attribute since
•
An
instance of a relationship set is a set of relationships, a snapshot of the
relationship set at some instant in time
Example:
An Instance of the Work_In Relationship Set

The entity sets
participating in a relationship set need not be distinct

Additional Features of the ER Model
•
Key constraints
•
Participation constraints
•
Weak entities
•
Class Hierarchies
Key Constraints
•
A Manages relationship
set
–
A single employee is allowed to manage more
than one department
–
Each department has at most one manager
•
ch department’s entity appears in at
most one Manages relationship in any allowable instance of Manages

An Instance of the Manages Relationship Set
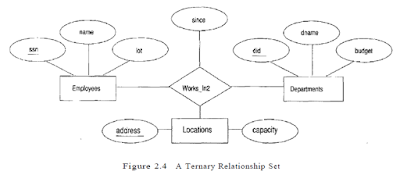
Key Constraints for Ternary Relationships

Participation Constraints
Suppose that every department is required to have a
manager

Example: Manages and Work_In

Weak Entities
•
A weak Entities can be identified uniquely
only by considering some of its attributes in conjunction with the primary key
of another entity
•
Employees can purchase insurance policies to
cover their dependents
•
Restrictions
–
One owner entity is associated with one or
more weak entities
–
Weak entity set must have total participation
in the identifying relation set

Class Hierarchies
•
Classifying entities in an entity set into
subclasses
•
A class hierarchy can be view in one to two
ways:
o
Specialized into subclasses
o
Generalized by a superclass
•
Overlap constraints determine whether two
subclasses are allowed to contain the same entity of their superclass
•
Covering constraints determine whether the
entities in the subclasses collectively include all entities in the superclass

Aggregation

A relationship between a collection of entities and
relationships
à
Aggregation allows us to indicate that a relationship set participates in
another relationship set
Entity & Attribute
Should a property be modeled as an attribute or as an
entity set?
Ex. Adding address information to the employee
entity set
à 2
options:
–
Add an attribute address
•
Record only one address per employee
–
Create en entity set address :
•
We have to record more than one address for
an employee
•
We want to capture the structure of an
address in our ER diagram
Ex. Break down an address into city, state, country, and
Zip code
Example: Entity & Attribute
Entity & Relationship
Binary and Ternary Relationships

•
An employee owns several policies
•
Each policy is owned by several employees
•
Each dependent is covered by several policies
Aggregation & Ternary Relationships
Each sponsorship is monitored by at most one employee
Conceptual Design for Large Enterprises
•
The process of conceptual design consists of
more than just describing small fragments of the application in terms of ER
diagrams
•
Large enterprise requires more than one
designer, used by a number of user groups
•
ER is easily to be understood by many people
who provide input to the design process
Design Process
•
Design process’s important aspect:
–
Methodology to structure the development of
the overall design
–
Ensure that the design take into account
•
All user requirements
•
Consistency
•
Approach1
–
Consider on various requirements of user groups
–
Resolve any conflicting requirements
–
Finally generate a single set of global
requirements
àGenerating
the single set is a difficult task
•
Approach2
–
Develop separate conceptual schemas for
different user groups
–
Integrate all the conceptual schemas
•
Establish correspondences between entities,
relationships, and attributes
•
Resolved numerous kinds of conflicts
•
Unavoidable case: the user demand access to
heterogeneous data sources
The Unified Modeling Language (UML)
•
Many approaches to end-to-end software system
design
–
Steps from identifying the business
requirements to the final specifications for a complete application
•
Workflow, user interfaces, …
•
UML is a popular approach
–
Attractive feature: constructs can be drawn
as diagrams
–
Broader spectrum of the software design
process than the ER model
•
Business modeling: describes business process
involved in the software application being designed
•
System modeling: identifies the requirements
for the software application (database requirement)
•
Conceptual modeling: provides many constructs
that parallel the ER constructs
•
Physical modeling: provides pictorial
representations for physical database design choices (creation of table space
and indexes)
• Hardware
system modeling: UML can be used to describe hardware configuration used for
the application
Diagrams in UML
•
Use case diagrams: describe the actions
performed by the system in response to user requests
•
Activity diagrams: show the flow of actions
in a business process
•
State chard diagrams: describe dynamic
interactions between system objects
•
Class diagrams: similar to ER diagrams
–
More general : model application entities,
and logical relationships in addition to data entities and relationships of ER
–
UML class diagrams corresponds closely to the
tables created by mapping an ER diagram
•
Database diagrams:
–
Show how classes are represented in the
database
–
Contain additional detail about the structure
of the database (integrity constraints and indexes), detail specific to the
relational model, and physical design choices
•
Component diagrams: describe storage aspects
of the database (table spaces and database partitions), and interface to
applications that access the data
•
Deployment diagrams: show the hardware
aspects of the system






0 comments:
Post a Comment